With the increasing digitalization of personal data and stricter data privacy regulations worldwide, ensuring robust data protection has become a non-negotiable for businesses. In India, the Digital Personal Data Protection Act (DPDPA) sets a new standard for how personal data should be processed, stored, and protected. To comply with this Act and similar regulations across the world, organizations need to invest in comprehensive DPDP solutions. But what exactly should a good DPDP solution encompass? This blog will explore the key must-haves for an effective DPDP solution, from managing consent to ensuring data transparency and security. The DPDP Act emphasizes on upholding the data privacy rights of individuals, so a DPDP compliance solution should be able to help businesses honor that.
At IDfy, when we started a discovery of the DPDP compliance we came across many insights. Overall we realized that organizations have never been structuring their systems or processes keeping consent in mind. So unfortunately, very often, the left hand does not know what the right hand is doing.
Here’s what a DPDP solution must have
1. Consent Governance and Lifecycle Management
Under the DPDPA, one of the most crucial principles is ensuring that individuals (referred to as data principals) have control over their personal data. Consent must be informed, freely given, specific, and revocable at any point.
Key Features:
- Granular Consent Collection: A good DPDP solution should support the collection of consent at multiple levels, ensuring that data principals have clear choices about which personal data they are willing to share and for what purposes.
- Consent Lifecycle Management: Managing consent doesn’t stop at collection. An ideal solution will help data fiduciaries track and log the entire lifecycle of consent for each purpose- when it was given, revoked, updated, or re-consented. This is critical for auditing and regulatory compliance to ensure accountability.
- Multilingual Support: In diverse countries like India, consent notices must be accessible in multiple languages. Supporting translations and transliterations ensures that individuals fully understand what they are consenting to, regardless of language barriers.
- Consent Revocation: Data fiduciaries should be able to use a DPDP solution to setup processes for consent withdrawal/revocation. These processes should also be able to notify data processors in case a data principal has decided to revoke their consent.
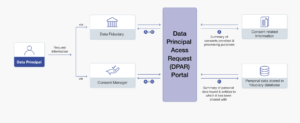
2. Automated Data Principal Access Request Management
The DPDPA empowers data principals to access, review, and request deletion or rectification of their personal data. These rights create a strong need for efficient management of Data Principal Access Requests (DPAR).
Key Features:
- Map out data processing activities specific to data type: A DPDP solution should have the capability to assign the processing of certain data to certain data processors. This can also be extended to assigning certain journeys to specific data processors too.
- Self-Service Portal: A user-friendly portal where data principals can easily submit access requests, review their data, and raise queries is essential. This empowers users to exercise their rights without complex interactions. Just like those email unsubscribe pages – but on steroids.
- Automated Workflow: Automation in handling requests ensures prompt responses and reduces manual effort, ensuring that organizations meet the regulatory timelines for request processing.
- Request Tracking and Status Updates: Keeping data principals informed about the status of their requests through real-time tracking, updates, and expected resolution dates fosters transparency and builds trust.
- Secure Data Retrieval and Delivery: When responding to data access requests, organizations must ensure that personal data is securely retrieved and delivered, adhering to encryption standards to avoid data breaches during the process.
3. Data Processor and Third-Party Management
In the modern business landscape, organizations rarely process all personal data in-house. Third-party data processors are involved, which adds a layer of complexity when it comes to ensuring compliance with data protection regulations.
In more candid words, managing consent across sub-processors is a minefield.
Key Features:
- Data Processor Inventory: A robust DPDP solution should allow organizations to maintain an updated inventory of all data processors and sub-processors involved in handling personal data. This includes tracking the type of data being shared, the purpose of processing, and relevant contracts.
- Real-Time Monitoring: A solution that enables ongoing monitoring of data processors’ activities helps ensure that third parties are complying with DPDPA regulations at all times.
- Processor Compliance Audits: Regular audits and reports on the data processor’s adherence to regulations provide an additional layer of protection and ensure accountability throughout the data lifecycle.
We at IDfy recently attended a DPDP workshop held by MeitY where we learnt about the challenges of ensuring data accuracy while maintaining a data inventory. For instance, if a data breach occurs, you need the correct contact details of your customers to inform them so they can respond accordingly. At the time of company mergers or collaborations, data fiduciaries should allow data principals the right to disallow their data from being transferred or deleted. Your customers will surely thank you for it!
4. Records of Processing Activities (RoPA) Automation
Maintaining accurate and up-to-date Records of Processing Activities (RoPA) is a key requirement of many data privacy laws, including the DPDPA. This document provides an overview of how, why, and where personal data is being processed, and by whom.
Key Features:
- Automatic RoPA Generation: A good DPDP solution should automate the generation and maintenance of RoPA, ensuring that it is always up to date. This reduces manual effort and the risk of errors.
- Data Mapping: The solution should be able to map personal data fields to their associated processing purposes and data processors. This ensures that organizations have a clear view of their data flows and can quickly identify potential compliance gaps.
- Compliance Reporting: Regular reports that can be used for internal reviews or shared with regulators during an audit are essential for proving that data processing activities are compliant.
5. Security, Encryption, and Data Integrity
Data security is paramount when handling personal data. The DPDPA and similar regulations require organizations to implement technical and organizational measures to protect personal data from unauthorized access, loss, or corruption.
ISO and SOC 2 certifications go a long way in establishing the security credentials.
Key Features:
- Encryption Standards: Strong encryption methods, such as SHA-256, should be used to secure personal data both in transit and at rest. This protects sensitive data from unauthorized access during its lifecycle.
- Immutable Data Storage: Solutions that provide version control and immutable data storage ensure that once personal data or consent records are stored, they cannot be tampered with or deleted. This is critical for compliance and legal purposes.
- Tamper-Proof Consent Artifacts: Consent records must be tamper-proof, ensuring that they cannot be altered without proper authorization. This builds trust and provides robust proof of compliance during audits.
- Audit Trails: Detailed logs of all data access and modifications should be maintained to monitor and track unauthorized activities. This is vital for both compliance and operational security.
6. Compliance with Sector-Specific Regulations
In India, beyond the DPDPA, many sectors such as banking, insurance, and healthcare are governed by additional regulations. Solutions that cater to these industries must account for not only the DPDPA but also sectoral rules from entities like the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India (IRDAI).
For example, Banks are required to keep customer data for upto 8 years – this would override any DPDPA provisions for automatic consent revocation.
Key Features:
- Customizable Consent Management: Organizations should be able to customize consent forms to meet both general data protection regulations and industry-specific requirements. This includes identifying consents that are mandatory, revocable, or re-consentable based on the type of data being processed.
- Sector-Specific Processing Rules: Advanced solutions provide templates and tools to easily comply with sectoral regulations by setting specific rules for data processing and consent management.
7. Comprehensive Reporting and Analytics
Reporting is a crucial element of demonstrating compliance with data privacy laws. Organizations need to generate and analyze reports that provide insights into data processing activities, consent management, and compliance status.
Key Features:
- Compliance Dashboards: A real-time dashboard that provides insights into key performance indicators (KPIs) such as the number of consents collected, revoked, or updated is essential for data protection officers (DPOs).
- Request Processing Time Analytics: Insights into how long it takes to process data access requests or consent-related changes allow organizations to optimize their processes and ensure they are meeting regulatory timelines.
- Breach and Incident Reporting: Solutions should integrate breach and incident reporting systems to quickly assess the scope of data breaches and notify affected parties as required under the DPDPA.
Watch the full webinar on Processing the DPDP Act: What Data Processors Should Know
Privy: A DPDP Solution to Empower you Data Protection Officer (DPO)
In the evolving landscape of data protection, having a trusted solution provider can make all the difference. One such name that has consistently aligned itself with data protection best practices is Privy. Privy, by IDfy, offers a range of solutions designed to streamline compliance with privacy regulations like the DPDPA and help businesses manage their data privacy obligations more effectively.
Privy Products
- Consent Governance Platform (CGP): The Consent Governance Platform by Privy is tailored to handle complex consent management needs. It allows businesses to manage the entire lifecycle of consent, from collection and updates to revocation. CGP is designed to ensure compliance with data protection laws while providing transparency and control to data principals.
- Cookies Manager: This tool helps businesses handle cookie consent in a compliant and user-friendly way. With customizable cookie banners and deep integration with websites, the Cookies Manager ensures that businesses comply with cookie regulations while enhancing user experience.
- Inspect AI: Designed to be an AI-powered copilot for Data Protection Officers (DPOs), Inspect AI automates the assessment of digital journeys for privacy compliance. By identifying privacy gaps and generating compliance scores, it simplifies the often complex task of staying aligned with data protection regulations.
These solutions represent a holistic approach to managing consent and data privacy, addressing the core requirements of the DPDPA while providing businesses with the tools they need to stay compliant without overwhelming their resources.
How can a DPO conduct a Gap Analysis?
Is my organization privacy-first? Does my organization have the tech infrastructure for DPDP compliance and handle data privacy requests? Everything from data collection to monitoring to updation is not a one-time exercise that cane be done and forgotten for good.
Conclusion
The Digital Personal Data Protection Act marks a significant shift in how personal data is handled in India. Organizations aiming for compliance must look beyond traditional data protection measures and adopt comprehensive DPDP solutions that include robust consent governance, automation of data processing records, stringent security measures, and sector-specific compliance tools.
By ensuring that your DPDP solution incorporates these must-have features, you can effectively navigate the complexities of data protection laws while building trust with data principals and regulatory authorities alike.
FAQs: Things to Keep in Mind Before Integrating a DPDP Solution
- What are the key regulatory requirements companies need to be
aware of before integrating a DPDP solution?
Before integrating a DPDP solution, ensure that the platform aligns with the specific requirements of the DPDPA. Additionally, sector-specific regulations like those from the RBI or IRDAI might necessitate tailored consent management, data storage protocols, and compliance audits. - How can companies ensure the DPDP solution integrates well with
their existing tech infrastructure?
Make sure the DPDP solution you choose can integrate seamlessly with your existing systems such as CRM platforms, HR databases, and other data-processing systems. API compatibility is a critical factor for ensuring smooth integration without major system overhauls. - How will the solution handle multi-language consent notices and
communication?
For businesses with diverse language needs, ensure the DPDP solution supports multilingual capabilities. Consent notices must be presented in languages that your user base understands, and the translations should preserve the legal and contextual clarity of the original content. - What security features are built into the DPDP
solution?
Look for security features like encryption (both in transit and at rest), tamper-proof data storage, and robust audit trails. Make sure that the platform adheres to high security standards such as SHA-256 encryption and has clear protocols for handling data breaches. - How do companies ensure compliance with future regulatory
changes?
A good DPDP solution should be adaptable and regularly updated to meet evolving regulatory requirements. Make sure the vendor offers continuous updates and support to keep your system compliant with both current and upcoming regulations. - Will the DPDP solution provide real-time monitoring and
reports?
Real-time reporting and compliance dashboards are essential for monitoring your data protection efforts. These tools help identify potential compliance gaps and ensure that you are meeting legal deadlines for processing data requests and maintaining records. - What is the total cost of ownership for a DPDP
solution?
Beyond the initial setup, consider the long-term costs, including licensing, ongoing support, and updates. Ensure that the solution offers a clear return on investment by reducing compliance risks, saving manual effort, and enhancing data protection efforts. - What is a consent artifact?
A consent artifact refers to a digital record of an individual’s data which is maintained. It acts
 IND
IND ID
ID PH
PH

